現代の領域で 食品包装, 熱成形機が極めて重要な役割を果たします, 効率的で魅力的なパッケージングソリューションを提供することを目的とした企業に汎用性の高いソリューションを提供する. このガイドは、食品包装用の熱成形機の複雑さに深く潜ります, その種類を調べる, コンポーネント, 材料, プロセス, 利点, 適切なマシンを選択するための考慮事項.
熱成形とは何ですか?
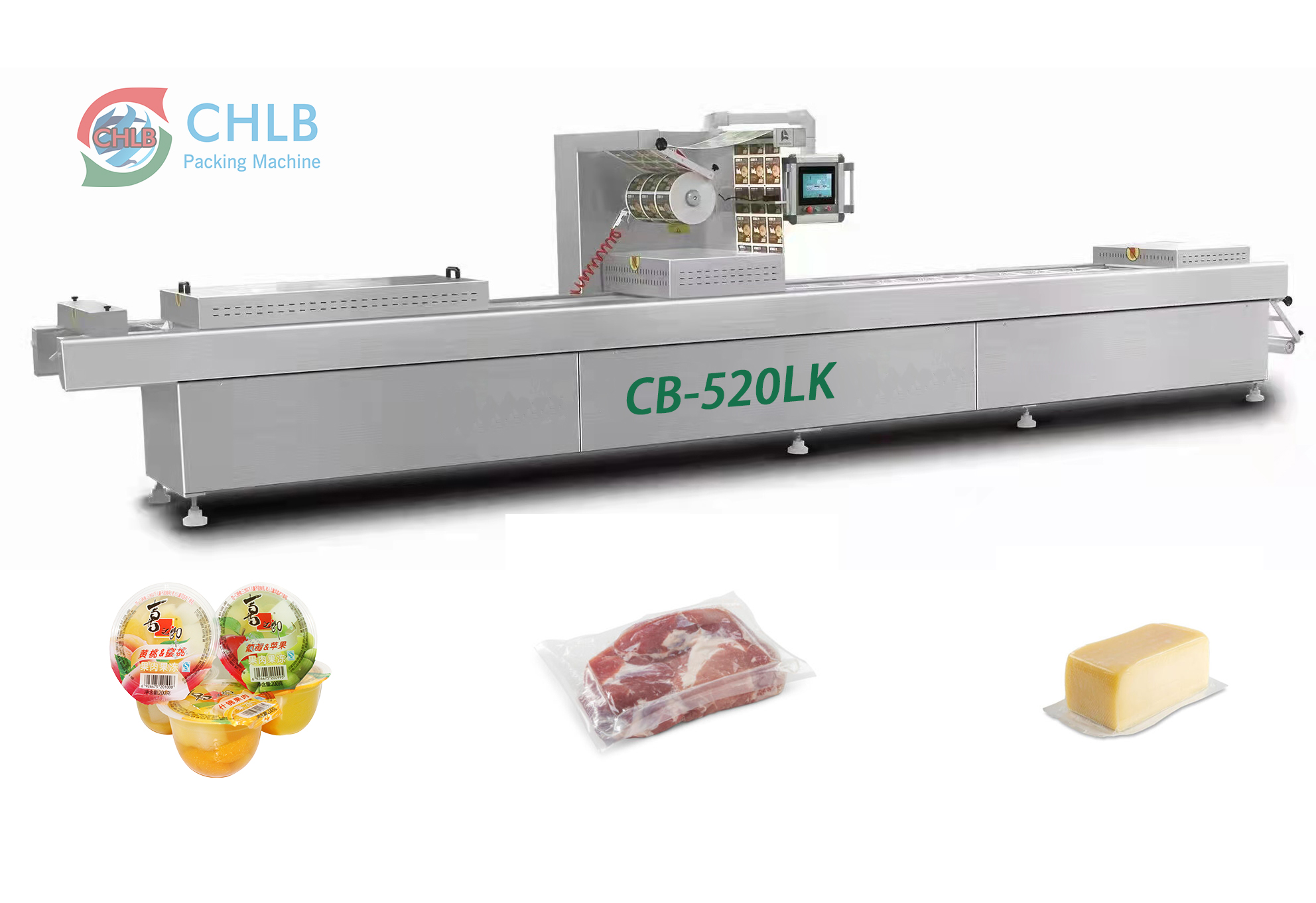

Thermoformingは、包装で広範囲に使用される製造プロセスです, 熱可塑性シートが柔軟な形成温度に加熱される場合, 金型を使用して特定の形状に形成されます, 最終製品を作成するためにトリミングされました. この方法は、カスタムパッケージソリューションの生産における汎用性と費用対効果のために広く採用されています.
熱成形機の種類
真空形成マシン
真空形成には、プラスチックシートが柔軟になるまで加熱することが含まれます, その後、真空圧を使用して型の上に成形します. この方法は、トレイのような浅い部品を生産するのに理想的です, ブリスターパック, そして、熱成形パッケージで使用されるクラムシェル.
真空熱成形機は、カスタムシェイプとサイズを効率的に作成できるため、さまざまな食品の包装に広く使用されています.
圧力形成マシン
圧力形成は、標準的な真空形成よりも、真空と圧力の両方を利用して、より詳細で耐久性のある部分を作成する. 複雑なデザインや厚い材料に適しています, 拡張された美学と構造的完全性を提供します. これらのマシンは、より高いレベルの耐久性と精度を必要とする堅牢な食品包装ソリューションを生産するのに理想的です.
ツインシートサーモフォーミングマシン
ツインシート熱酸加工には、2枚のシートを同時に加熱して形成することが含まれます, 次に、それらを一緒に密封して、二重壁の部分を作成します. この方法は、中空の空間または断熱特性を備えた製品の作成に使用されます. 断熱またはバリアの特性を必要とする容器とトレイの生産に使用されます, 熱成形食品包装の機能を強化します.
熱成形機の重要なコンポーネント
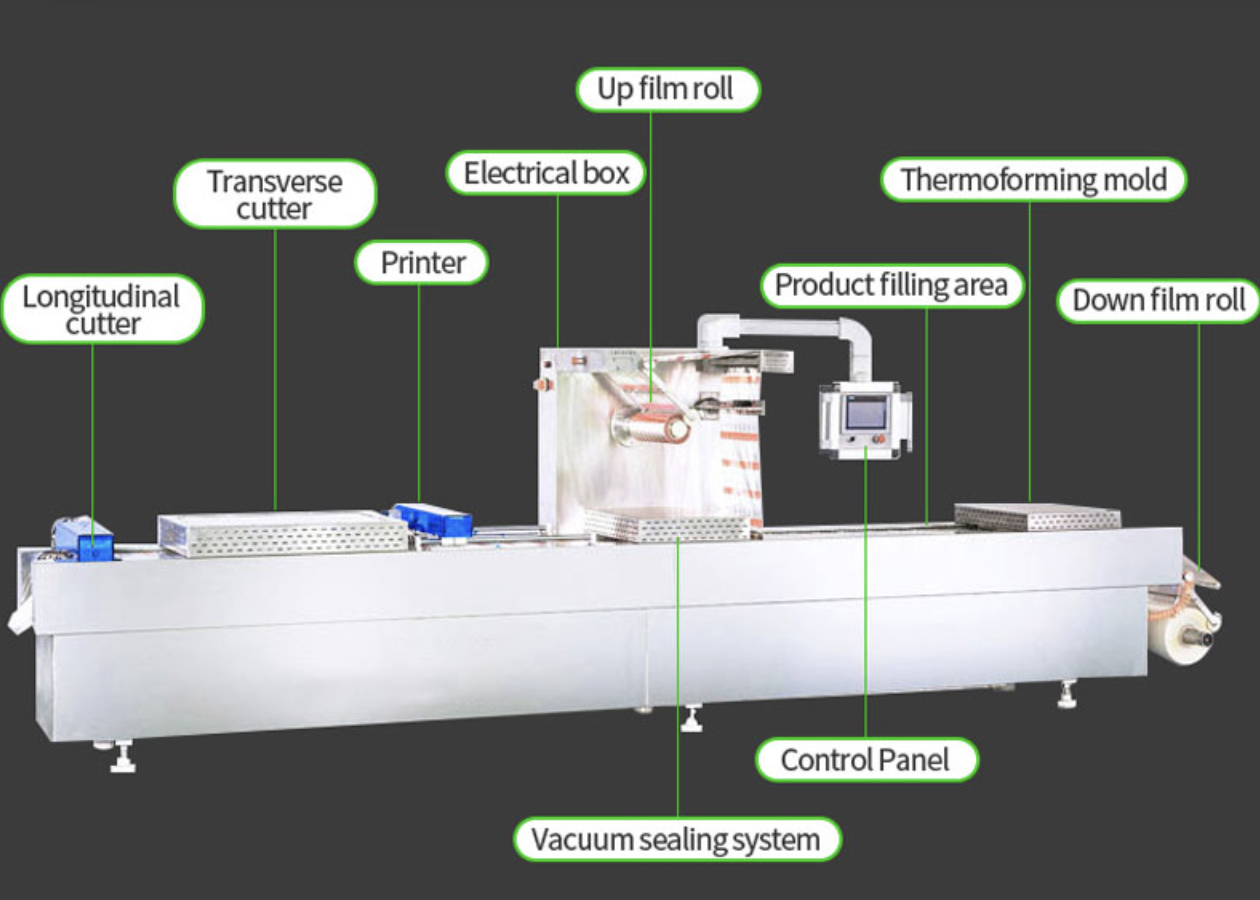
発熱体
熱成形機は、セラミックなどのさまざまな加熱要素を利用しています, 石英, プラスチックシートを均一に加熱するための赤外線ヒーター. 正確な温度制御は、一貫した形成結果を達成し、熱成形パッケージの品質を確保するために重要です.
ステーションの形成
ステーションの形成は、複雑さと能力が異なります, 特定のパッケージング要件に基づいて、成形の形状とサイズのカスタマイズを可能にする. 最新のマシンは、多様なパッケージングのニーズに対応するために、調整可能な金型と形成パラメーターを提供します, 単純なトレイから複雑な容器まで.
トリミングステーション
トリミングステーションは、形成された部品から余分な材料を除去するために切削工具を利用しています, きれいなエッジと正確な寸法を確保します. 熱成形食品包装で均一性と審美的な魅力を達成するためには、正確なトリミングが不可欠です, 製品のプレゼンテーションと機能の強化.
制御システム
高度な制御システムは、熱成形プロセスを自動化します, 効率を高め、人為的エラーを減らす. 直感的なユーザーインターフェイスは、マシンの操作とメンテナンスを簡素化します, 全体的な生産性とオペレーターの満足度の向上.
食品包装のための熱成形で使用される材料
ペット (ポリエチレンテレフタレート)
ペットはその明確さのために広く使用されています, 強さ, およびバリア特性, パッケージング飲料に適しています, サラダ, とベーカリーアイテム.
PP (ポリプロピレン)
PPは、水分と化学物質に対する優れた耐性を提供します, ヨーグルトカップのパッケージに最適です, デリコンテナ, および電子レンジの食品トレイ.
PS (ポリスチレン)
PSは軽量で多用途です, 肉トレイの包装に一般的に使用されます, 卵カートン, 使い捨ての食品容器.
熱成形プロセス
#1: 前処理
材料の選択: 適切な熱可塑性材料を選択することは、明確さなどの望ましい特性を達成するために重要です, 耐久性, そして、熱成形された食品包装のリサイクル性.
シート押し出し: 均一な厚さのプラスチックシートを押し出すと、熱成形プロセスの準備ができます, 製品の品質の一貫性を確保します.
#2: 形にする
加熱: 熱可塑性シートを最適な形成温度に加熱する, 成形のために柔軟にします.
成形: 真空または圧力を適用すると、加熱されたシートが希望の形状になります, 正確なパッケージングの寸法のために、金型の輪郭に適合します.
#3: トリミングと仕上げ
切断技術: 切削工具またはダイを使用して形成された部品から余分な材料をトリミングすると、熱酸加工された食品包装のきれいなエッジと均一性が保証されます.
品質管理: 厳格な検査とテスト手順の実装により、最終製品が品質基準を満たすことが保証されます, 顧客満足度と規制要件へのコンプライアンスを確保します.
食品包装における熱成形機の利点
熱成形は、柔軟性の観点から射出成形やブロー成形などの伝統的な方法を上回ります, 費用対効果, とスピード, それを好みの選択にします 食品包装アプリケーション.
- 費用対効果: Thermoformingは、他の成形方法と比較して、ツーリングコストを削減し、生産サイクルを速く提供します, 小規模から大規模な生産のためにそれを経済的にしています.
- 設計の柔軟性: カスタムシェイプを作成する機能, サイズ, テクスチャは、製品の可視性と消費者の魅力を高める革新的なパッケージデザインを可能にします.
- スピードと効率: Thermoformingマシンは、大量のパッケージを迅速に生産できます, 厳しい生産スケジュールと市場の需要を効果的に満たします.
- 強化された製品保護: Thermoformed Packagingは、水分に対する優れたバリア特性を提供します, 酸素, および汚染物質, 貯蔵寿命を延長し、製品の新鮮さを確保します.
適切な熱成形機を選択します
ニーズの評価
生産要件を評価します, 材料の好み, そして、あなたのビジネス目標と整合する熱成形機を選択するための望ましい出力ボリューム.
注目すべき主な機能
加熱能力などの要因を考慮してください, ステーション構成の形成, トリミングオプション, Aを選択するときの自動化機能 熱成形包装機.
予算に関する考慮事項
初期投資コストと長期的な運用貯蓄と生産効率のバランスを取り、熱成形食品パッケージのROIを最大化する.
メーカーの評判とサポート
選ぶ 評判の良い熱成形機のメーカーおよびサプライヤー 信頼性で知られています, テクニカルサポート, スムーズな運用と機械の長寿を確保するためのレスポンシブカスタマーサービス.
結論
熱成形機は、食品包装業界で不可欠なツールです, 比類のない汎用性を提供します, 効率, そして費用対効果. タイプを理解することによって, コンポーネント, 材料, 複雑なプロセス, 熱成形の利点, 企業は、パッケージング機能を強化し、熱成形食品包装ソリューションの進化する消費者の需要を満たすための情報に基づいた意思決定を行うことができます.
食品包装用の熱成形機のFAQ
1. 熱成形を使用して一般的にパッケージ化されている食品の種類?
Thermoformingは、肉などの製品の包装に広く使用されています, チーズ, ベーカリーアイテム, 新鮮な農産物, そして、保護的で魅力的なパッケージングソリューションを提供する能力により、すぐに食べられる食事.
2. 熱成形は、持続可能なパッケージングの慣行にどのように貢献しますか?
Thermoformingは、リサイクル可能な材料の使用と最適化された材料の使用を可能にします, 従来の包装方法と比較した環境への影響を減らす.
3. 真空形成と圧力形成マシンを選択する際の重要な考慮事項は何ですか?
真空形成は、浅い部品や低ボリュームの生産に適しています, 圧力形成は、熱成形食品パッケージの複雑なデザインと厚い材料の詳細と耐久性を高めます.
4. 熱成形機の自動化は、生産効率をどのように改善できますか?
自動化により肉体労働が減少します, エラーを最小化します, スループットを増加させます, より速い生産サイクルを有効にし、熱型の食品包装における一貫した品質.
5. 食品包装のための熱成形で材料の選択がどのような役割を果たしますか?
適切な熱可塑性材料を選択すると、パッケージが食品安全基準を満たすことが保証されます, 適切なバリアプロパティを提供します, 製品の貯蔵寿命とプレゼンテーションを強化します.















